“🔓Step into the world of thermal imaging! Explore the wonders with our top-quality infrared cameras🌡📸. See beyond the visible! #ThermalImaging”
An infrared camera, also known as a thermographic camera, captures and measures the invisible yet powerful radiation emitted from objects. Having an infrared camera helps differentiate heat levels on surfaces by detecting variations in infrared radiation and converting this data into thermal images or videos. Vital for various scientific, medical, and research applications, such as surveillance, night vision machinery operations, and gas leak detection, these devices enable us to witness aspects of our universe that are otherwise invisible to the naked eye.
Understanding Thermal Imaging
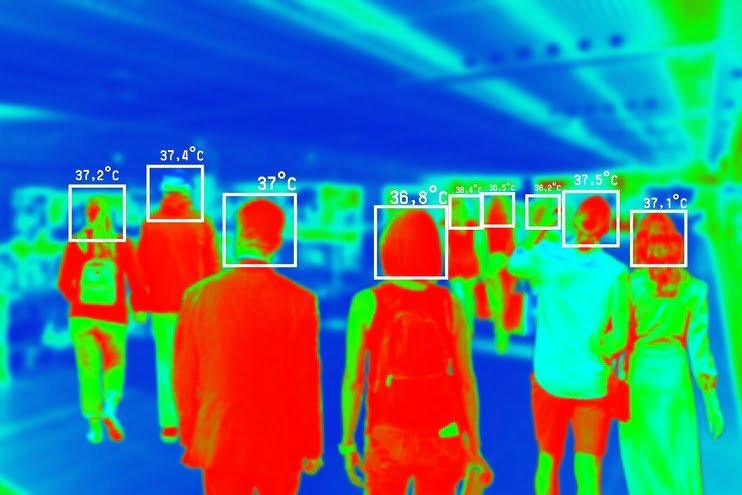
Thermal imaging technology works by detecting radiant heat emitted from objects and converting it into a visible image. A thermal imager uses infrared sensors to capture temperature differences within its field of view. Warmer subjects emit more infrared radiation and stand out against cooler backgrounds due to varying degrees of infrared light intensity. This information is processed into a visual spectrum, resulting in an image displaying shapes defined by their relative temperatures.
Applications of Thermal Imaging
Thermal imaging plays a significant role across diverse industries. In manufacturing, it helps identify failures in electrical systems. In the medical field, thermal imaging can aid in early disease detection by visualizing irregularities in body temperature. Emergency services employ this technology during rescue operations under conditions of low visibility, such as smoke or darkness. Wildlife researchers use these systems for nocturnal animal studies and population monitoring. Additionally, it is widely used in surveillance, enhancing security by detecting hidden objects or individuals at night.
Advantages of Using Infrared Cameras for Thermal Imaging
Advancements in infrared camera technology have significantly enhanced the ability to detect heat variations. Sensitive thermal sensors and infrared imaging methods are instrumental in various applications, from medical diagnosis to detecting home insulation leaks or fire spots during forest fire surveillance. This technology allows us to exploit environmental resources more efficiently, promote safety measures effectively, and initiate early health interventions, underscoring its versatile importance in modern life.
Infrared cameras are crucial in low-light environments due to their heat-sensing capabilities. Unlike traditional cameras, they capture images based on thermal radiation instead of visible light, making it feasible to distinctly signal differences between warm and cold areas even in pitch darkness. This is a principal advantage during night surveillance or investigations. They are vital for wildlife research, security applications, dark alley monitoring, and military operations, ensuring safety while providing insights into unseen occurrences.
Infrared cameras can effectively penetrate through smoke or fog, employing a technology that operates beyond the limitations of human vision. They capture images using infrared radiation rather than visible light, thus providing visibility regardless of poor weather conditions. This invaluable ability makes infrared cameras crucial during structural firefights, surveillance operations, marine navigation, and other specific cases where traditional forms of vision often fail.
Harnessing the Full Potential of Infrared Cameras
To harness the full potential of infrared cameras, users should follow certain tips for optimal performance. Reading the instruction manual thoroughly helps understand the device’s functioning. Safety measures should be strictly followed to prevent accidents. Regular maintenance and cleaning ensure longevity. Exploring digital guides or tutorials can provide additional insights. Using the device proficiently and optimizing functions as needed without overloading capacity promotes sustainability. Any malfunctions should be reported, and professional repair sought instead of unsophisticated fixes, which may aggravate issues further.
Modern optimization techniques have significantly advanced infrared cameras for thermal imaging. Key innovations include improved resolution, aspect ratio adjustments, and real-time data analysis algorithms. Enhanced detection ranges reduce false positives, while adaptive thresholding helps balance sensitivity with environmental variables. Calibrated colour palettes result in clearer image representation of the emissions spectrum, facilitating careful interpretation of the thermal scenarios captured.
The Future of Thermal Imaging and Infrared Cameras
Recent advancements in thermal imaging and infrared camera technology have transformed numerous industries. Emerging trends include higher resolution, integration with AI for smart detection, compact designs for mobility, drone usage, and cost reduction. Ultra-sensitive sensors can now detect minimal temperature differences, providing superior accuracy. AI allows for the recognition of specific heat signatures, enhancing precision in fields like security and healthcare. Trends are directed towards widespread accessibility and usability, with personal smartphones even integrating this technology, showing its growing applicability.
FAQs
What is an infrared camera used for?
An infrared camera is primarily used for detecting heat in various applications. It captures and creates an image by utilizing the invisible infrared radiation emitted by objects, especially warm ones. Infrared cameras are crucial for professionals like firemen to identify hot spots during fires, electricians to find overheating wires or systems, building inspectors to detect insulation flaws, astronomers studying celestial bodies, and wildlife researchers tracking nocturnal animals’ activities unseen by the naked eye.
What is the difference between an infrared camera and a thermal camera?
An infrared (IR) camera and a thermal camera are distinct technologies that detect different types of light. An IR camera specifically captures images using the infrared light spectrum, often used for night vision in low-visibility situations. A thermal camera creates an image based on detecting differences in heat emitted by objects within its field of view. While both can operate in darkness or through obstructions like fog and smoke, they serve different functionalities due to their unique capabilities.
Can infrared see through walls?
Infrared technology cannot directly see through solid objects such as walls. It operates by detecting heat in the form of thermal radiation that objects, particularly living organisms, naturally emit. If an object’s or individual’s heat signatures are strong enough and the wall material is thin enough, it may somewhat detect these signatures but not discern images behind the wall. Therefore, infrared can sense rather than “see” through certain barriers depending on their composition and thickness but won’t offer clear visibility.
How far can an infrared camera see?
The range of an infrared camera largely depends on its specific features and quality, including lens configuration, detector performance, resolution, and atmospheric conditions. Generally, high-quality models can detect heat signatures over a mile away. However, discernable identification reduces dramatically with distance usually within 100-200 feet for most commercial cameras. Therefore, exact distances vary, but identified point sources or larger objects should be fairly close to achieve good visibility and clear picture quality.